Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
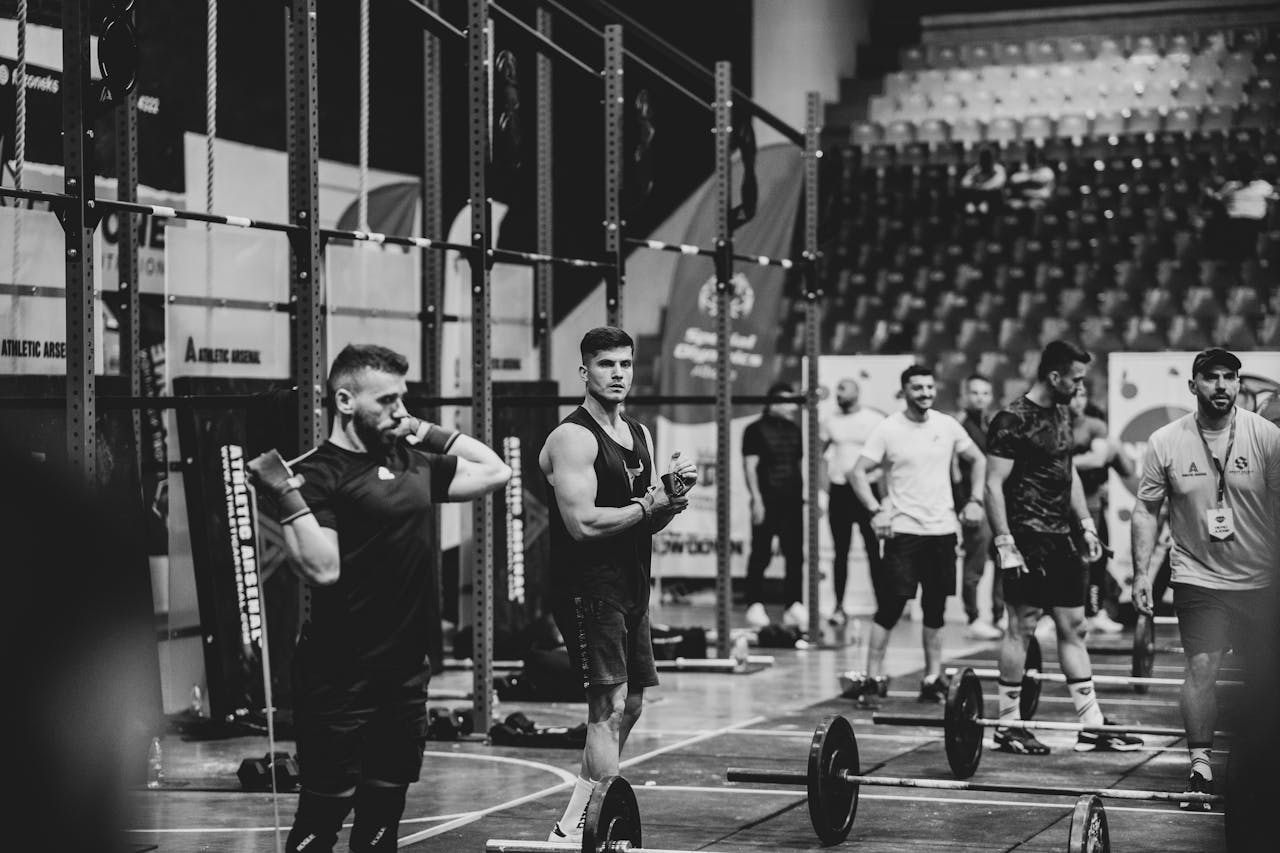

In sports and physical form, high -level performance is never built on a single physical quality. Instead, it’s the interdependence of performance -related fitness components-as strength, power, speed, agility, flexibilityAnd endurance– This creates the edge of an athlete.
As underlined in Sports packaging model from Bompa & Carrera and supported by scientific studies evaluated by peersOptimizing a component often improves several others. This article gives an overview of experts of the way these components relate and how to train them effectively.
These are essential physical features for Specific sport performance. Unlike health components (for example, bodily composition, basic cardiovascular health), Performance features are responsible for:
They must be trained together, not in isolation.
Definition: The ability to generate force against resistance (force × distance).
Why is it important: Strength is the foundation of development power,, speedAnd injury prevention.
“Force is the adaptation that leads to all the other adaptations that are really close to your heart.” – Charles Staley
Types of training:
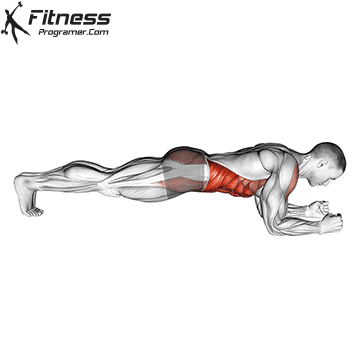
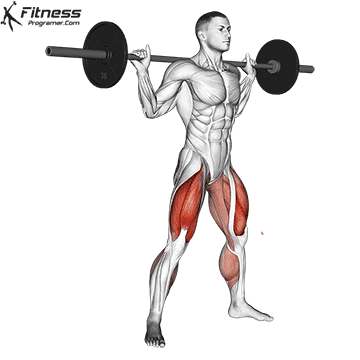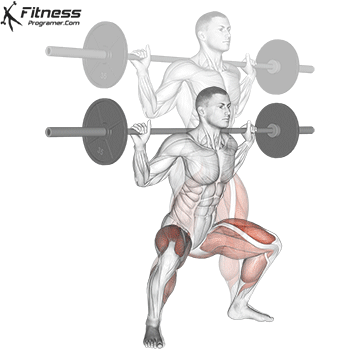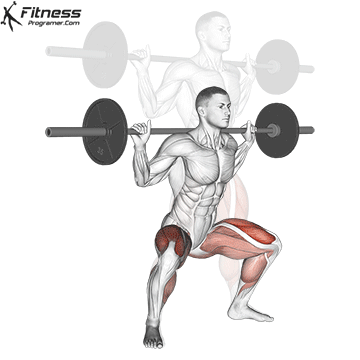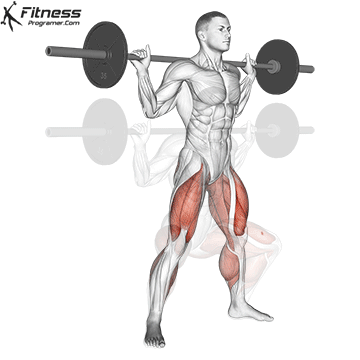
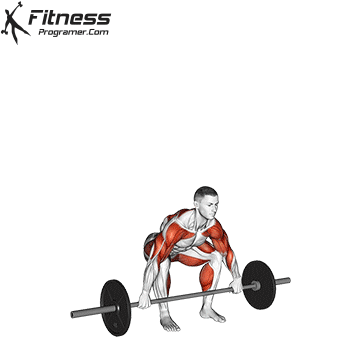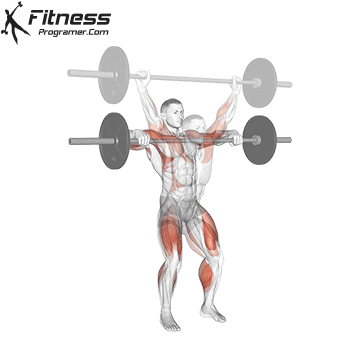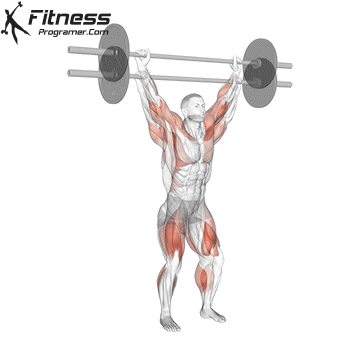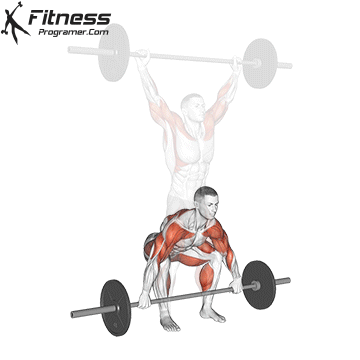
Evidence: Strength training Reduces the risk of injuries in young athletes (Faigenbaum and Schram, 2004).
Definition: Power = strength × distance ÷ Time
Key line: Combination strength with speed of execution.
Examples of application:
Search overview: Increased power is more linked to development that the speed of travel alone (Bompa, 2015).
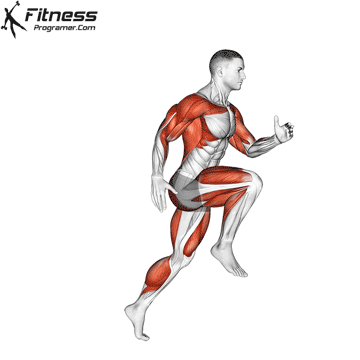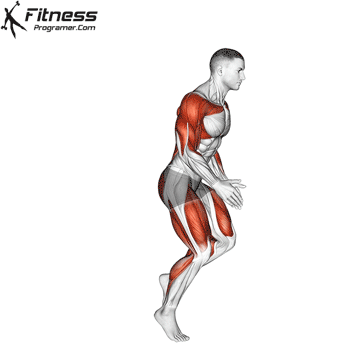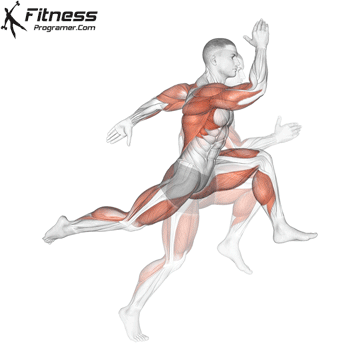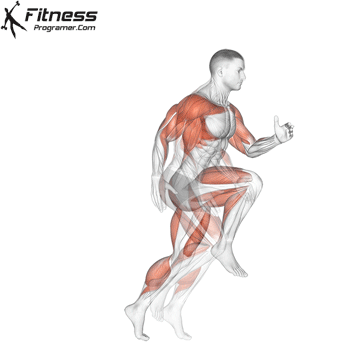
Definition: Speed = Distance ÷ Time
Sub-components:
Training dependence: Strong and powerful muscles improve acceleration and high -end speed.
Note: Speed is forceless And refined with coordination.
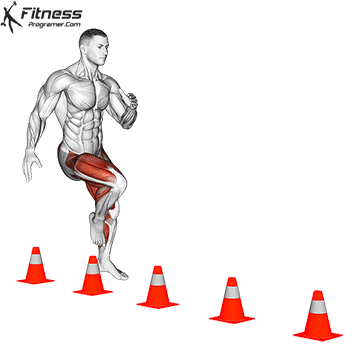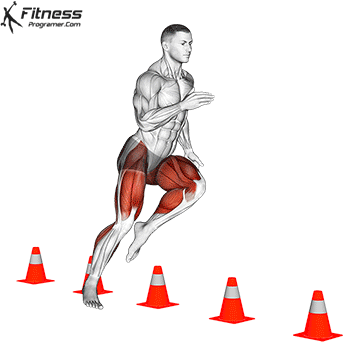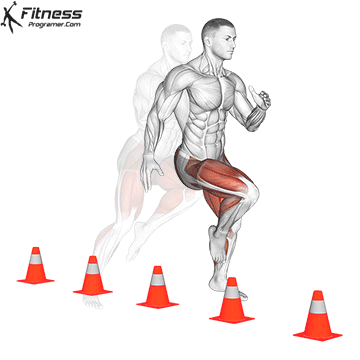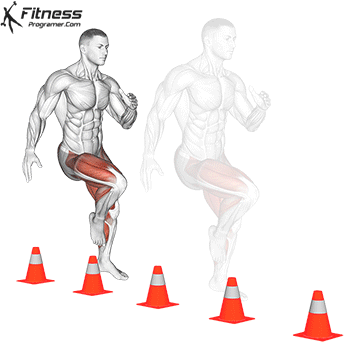
Definition: The ability to decelerate and effectively change management.
Relies on:
Training advice: Avoid repeating the same exercise all year round. Agility training must include Specific variation in sport To avoid trays.
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Continuous tension | Planks, climb |
| Isometric | Static holders, isometry |
| Repetitive dynamic | Rowing, high representation training |
| Short rest / high effort | Circuit training, football |
These types exist on a continuum and overlap frequently according to sports requests.
Dynamic flexibility:
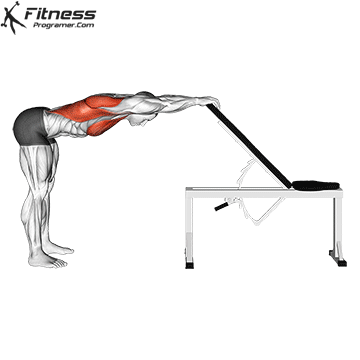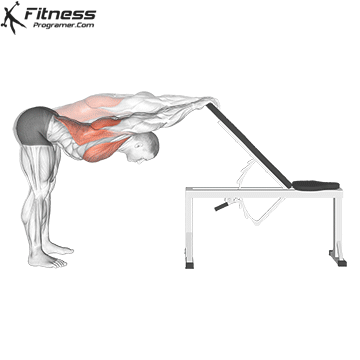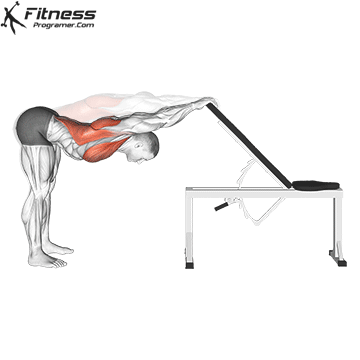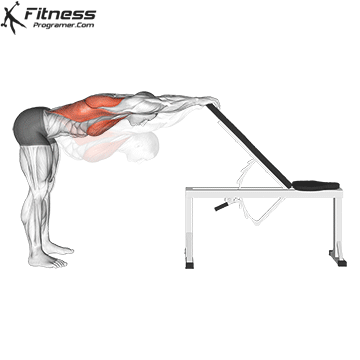
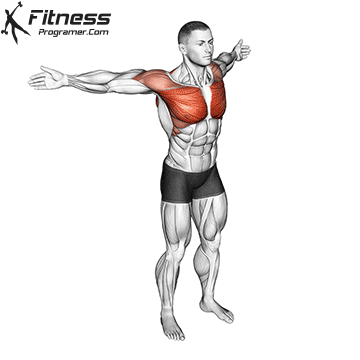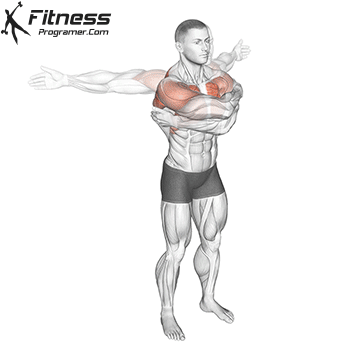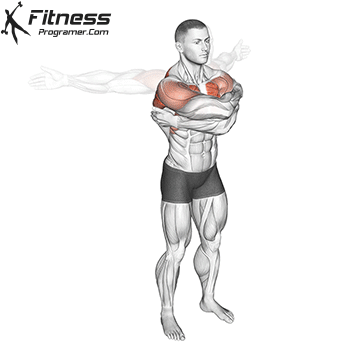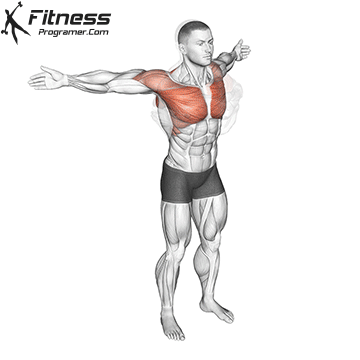
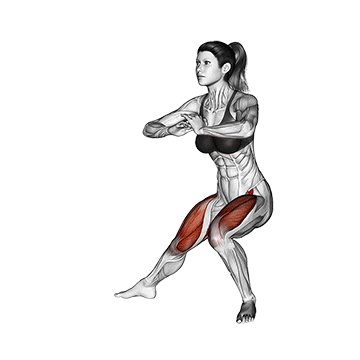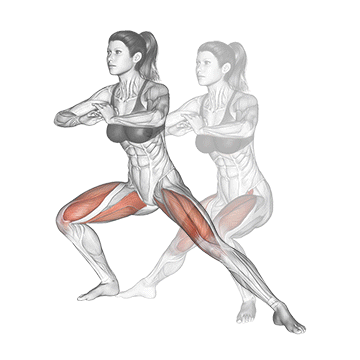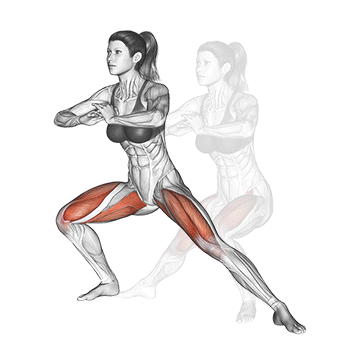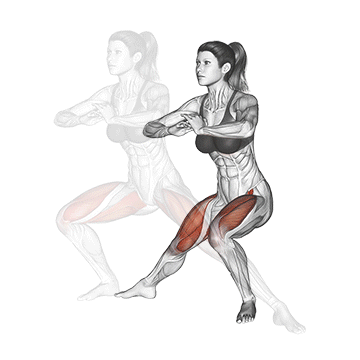
Static flexibility:



Scientific warning:
Pre-exercise static stretching can Reduce strength and power For up to an hour (Evetovich et al., 2003; Young and Behm, 2003).
Specific use of the context:

Coordination includes:
Coordination is this connects raw physical power to functional athletics. All athletes benefit from the integration of exercises that improve timing and neuromuscular control.
1. Specificity: Train according to your sport or goal.
2 Overload:: Gradually increase intensity or volume.
3. Variation: Tying the stimulus to avoid the tray.
4. Recovery: Respect the effects of residual training – each quality of fitness quality at a different rate.
| Adaptation | How long it lasts (medium) |
|---|---|
| Strength | 30+ days |
| Endurance | 15-30 days |
| Speed | 5 to 10 days |
Performance fitness components do not work in silos. Your ability to sprint, jump, change direction or recover fatigue is determined by the way Well, your whole physical system works together.
Whether you are coach, athlete or recreational trainee, construction programs that are addressed strength, power, speed, endurance, flexibility and coordination In a cohesive and progressive way is the path of performance.
References